Node, Express, and APIs
What is Node and when should I use it
What is node.js?
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine an event-based, non-blocking, asynchronous I/O runtime that uses Google’s V8 JavaScript engine and libuv library.
V8 Engine is the open source JavaScript engine that runs in Google chrome and other Chromium-based web browsers
You can test if node.js is installed by typing node -v
npmis the node package manger for node.
npm install -g jshint
^ This will install jshint package globally.
npm init -y
^ Will create and auto-populate a package.json file in the same folder.
The
node_modulesfolder shouldn’t be checked in to version control, and can, in fact, be re-created at any time by runningnpm installfrom within the project’s root.
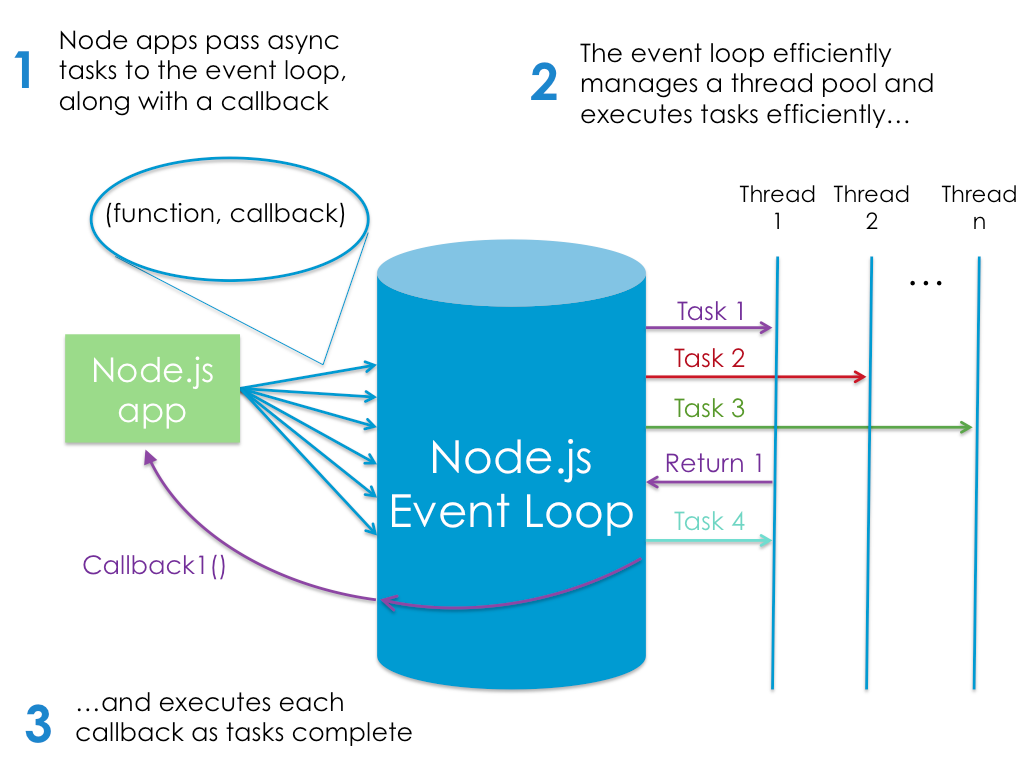
Node.js single threaded & event driven. ` When a new request comes in the server will start processing it. If it then encounters a blocking I/O operation, instead of waiting for this to complete, it will register a callback before continuing to process the next event`
Downsides
- Intensive operations could potentially crash
- Developers dislike callback based style of coding that js imposes
Hello World
const http = require('http');
http.createServer((request, response) => {
response.writeHead(200);
response.end('Hello, World!');
}).listen(3000);
console.log('Server running on http://localhost:3000');
Node.jsis suited for building applications that require some form of real-time interaction or collaboration. (i.e. chat sites, or apps such as CodeShare, building APIs, Data Streaming.)
Express.js
Express.jsis a Node.js web framework that has gained immense popularity due to its simplicity. It has easy-to-use routing and simple support for view engines, putting it far ahead of the basic Node HTTP server.
Express does this out of the box
| name | definition |
|---|---|
| routing | This is how /home /blog and /about all give you different pages. Express makes it easy for you to modularize this code by allowing you to put different routes in different files. |
| Middleware | If you’re new to the term, basically middleware is “software glue”. It accesses requests before your routes get them, allowing them to handle hard-to-do stuff like cookie parsing, file uploads, errors, and more. |
| views | Views are how HTML pages are rendered with custom content. You pass in the data you want to be rendered and Express will render it with your given view engine. |
Express Application structure
| name | definition |
|---|---|
| Routes | Where you’ll put your router files. The generator creates two files, index.js and users.js, which serve as examples of how to separate out your application’s route configuration. |
| Views | The views folder is where you have the files used by your templating engine. The generator will configure Express to look in here for a matching view when you call the render method. |
| App.js | It sets up your Express application and glues all of the different parts together. Let’s walk through what it does. |
server.js needs 3 parts
// new route
app.get(route, function)
// function that runs fromt the route
function doStuff(req, res){
res.json(foo) // returns json file
res.send(text) // sends text
}
// constructor so you know what to return from the server
function Construct(obj, data){
this.potato = obj
this.carrot = data.whatIWant
}
// turns on server listens
app.listen(PORT, () =>{
console.log(`Listening on ${PORT}`)
})