Linked lists
Linked List- is a sequence of Nodes that are connected/linked to each other.
Types of linked lists -
- Singly - means that there is only one reference, and the reference points to the Next node in a linked list.
- Doubly - means that there is a reference to both the Next and Previous node.
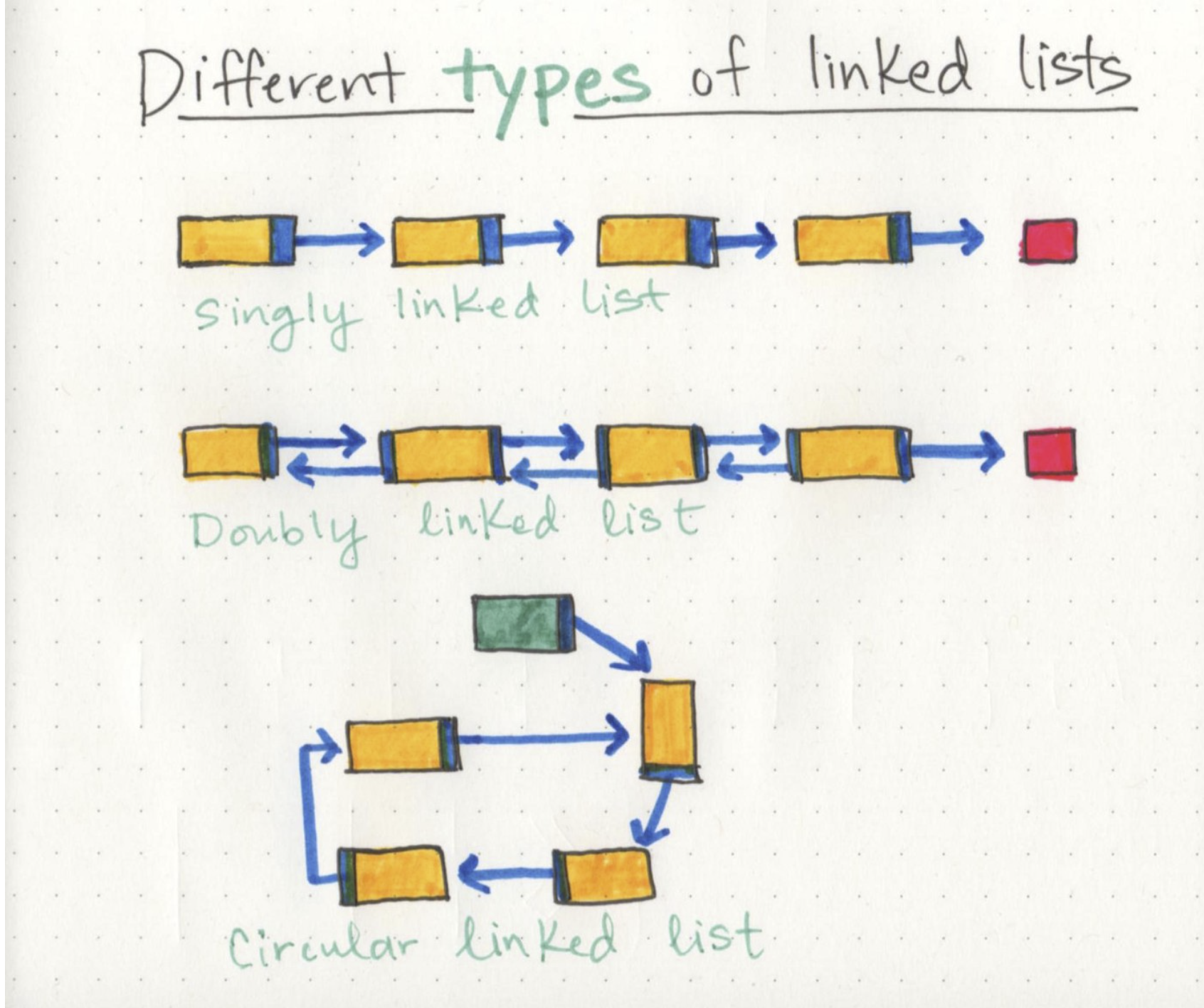
Notables
-
When traversing a linked list you are not able to use a foreach for loop. - Use the Next value in each node
- Best way to approach a traversal is through the use of a
whileloop. You can check that theNextnode in the list is null.
Parts of Linked Lists
- Nodes - Elements of the lists
- Head - Starting point
- Null - end of the list; usually an empty value.
NullReferenceExceptiongets thrown trying to traverse on a node that is null
Current- will tell us where exactly in the linked list we are and will allow us to move/traverse forward until we hit the end.
# if linked list includes a value
def Includes(value):
Current = Head
while Current != None:
if Current.Value == value
return True
Next(Value)
return False
Big O of Time for includes would be O(n) = n represents the number of nodes in the list.
Big O of space for includes would be O(1) = there is no additional space being used than what is already given to us with the linked list input.
Big O Notation
Big ONotation is a way of evaluating the performance of an algorithm.
For linked lists there is two types of Big O equations to remember are O(1) and O(n).
-
An
O(1) functiontakesconstant time, which is to say that it doesn’t matter how many elements we have, or how huge our input is: it’ll always take the same amount of time and memory to run our algorithm. -
An
O(n) functionislinear, which means that as our input grows (from ten numbers, to ten thousand, to ten million), the space and time that we need to run that algorithm grows linearly.