Chapter 2: “Text” (pp.40-61)
| name | description | example |
|---|---|---|
| Headings | There are 6 level of headings: <h1> <h2> <h3> <h4> <h5> <h6> | <h1></h1> - Main headings |
| Paragraphs | Consists of one or more sentences | <p></p> |
| Bold | Make the characters bold | <b> |
| Italic | Used to say something in a different way then the surrounding context. | <i> |
| Superscript | Suffixes of dates or mathematical concepts like rasing a number | <sup> |
| Subscript | Commonly used for foot notes or chemical formulas | <sub> |
| White space | In order to make code easier to read pages often add extra spaces on a new line | |
| Line breaks | It will show the paragraph or header on a new line | <br /> |
| Horizontal rules | To create breaks between themes - such as change of topic | <hr /> |
| Strong | Indicates the content has strong importance | <strong> |
| Emphasis | subtly changes the meaning of sentence. | <em> |
| Blockquote | Used for longer quotes that take up an entire page | <blockquote> |
| quotes | Is used for shorter quotes | <q> |
| abbreviation | For acronyms. Usually uses a title attribute on the opening tag | <p><abbr title=”example”>ex<abbr> |
| citation | When you are referencing a piece of work. | <cite> |
| Definition | First time you explain some new terminology. | <dfn> |
| Address | Contains contact details of the author | <address> |
| Insert | Show the content that has been inserted. Usually underlined | <ins> |
| Delete | Content usually has a strike through line. You can also use an <s> element | <del> |
Chapter 10: Ch.10 “Introducing CSS” (pp.226-245)
CSS - allows you to create rules that specify how the content of an element should appear.
| name | description | example |
|---|---|---|
| Selector | Which element the rule is applied to | p {} |
| Declaration | How the element referred to should be styled | {background-color: blue;} |
| Properties | Indicates the aspects of the elements you want to change | color: green; |
| Values | Specify the setting you want to use for the properties | color: green; |
External CSS
| name | description | example |
|---|---|---|
| link | Used to tell an HTML element where to find CSS | <link href=”css/styles.css” type=”text/css” rel=”stylesheet” /> |
Internal CSS
| name | description | example |
|---|---|---|
| Style Element | You can include CSS rules within you HTML page by placing them inside a <style> element. | <head><style type=”text/css”>body {font-family: arial;}</head> |
CSS selectors
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | matched element names |
| Class | matches the class attribute that is specified after a period. Cover multiple text. |
| ID | Matches the value of the one that is specified after the hashtag symbol. Used for specific parts of the page. |
| Child | matched the element that is a direct child of another |
| Descendant | Matches an element that is a descendant of another element ex: p a {} |
| Adjacent sibling | Matches the next sibling of another. |
| General sibling | Matches and element that is a sibling of another although it does not have to be the directly preceding element. |
How rules cascade - Last rule can override by Specifity and if you put ! after any property value it is most important. Specifity = Type>Class>ID
You should use external style sheets so that multiple web pages cna share, the site will load faster, you don’t have to change the rules on every page
Chapter 2: “Basic JavaScript Instructions” (pp.53-84)
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Script | is a series of instructions that a computer can follow one-by-one. | |
| Statement | each step in a script. Should end in a ;. These are instructions and should start on a new line. | |
| Code Blocks | statements that are surrounded by curly braces. They should not be followed by a semicolon. | |
| Comments | you should write comments explaining what your code does. | |
| Multi line | comments over multiple lines | starts with /* and ends with */ |
| Single line | anything that follows the two forward slash comments | // comment |
| Variable | Stores data temporarily in a script so it can work. The data changes or varies what each script does. | Var “variable name” = “value”; |
| Booleans | True or false values | true |
| numbers | handles numbers or integers. These are not written in quotes | 1 2 3 |
| String | consists of letters; values are immutable. Can’t be altered. | abc |
| Assignment operator | Remember that everything to the right of the equals sign is evaluated first | |
| Camel case | upper case that follows the word. js does not use spaces in var | |
| Concatenating | link (things) together in a chain or series | |
| floats | Decimal numbers | |
| multi-dimensional array | nested arrays within other arrays | [[ 3, 4, 5] + [3]] |
Expressions
an expression evaluates in to a single value.
- Expressions that are just assigned to a variable - var color = green;
- Expressions that use two or more values to return a single value - var area = 3 * 2;
Operators
Operators allow programmers to create a single value from one or more values.
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Assignment operators | Assign a value to a variable | color = ‘green’; |
| Arithmetic operators | Perform basic math | area = 3 * 2; |
| String operators | combine two strings | greeting = ‘hi’ + ‘molly’; |
| comparison operators | Compare two values and return true or false | = 3 > 5; pg 150 |
| Logical operators | Combine expressions and return true or false | buy = (5 > 3) && (2 < 4); pg 156 |
Arithmetic operators pg 76
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Addition | + | |
| Subtraction | - | |
| Division | / | |
| Multiplication | * | |
| increment | Adds one to the current number | ++ |
| Decrement | Subtracts one to the current number | – |
| Modulus | divides two values and returns the remainder | 10 % 3 = 1 |
*There is only one string operator, the + symbol
Example:
- var firstName = ‘ivy’;
- var lastName = ‘Stone’;
- var fullName = firstName + lastName;
Mainly used for personalized messages
Assignment, Comparison and Logical Operators
| keyword | Description |
|---|---|
| == | is equal to |
| != | is not equal to |
| === | strict equal to |
| !== | strict not equal to |
| > | greater than |
| < | less than |
| >= | greater than or equal to |
| <= | less than or equal to |
| && | logical and; test more than one condition |
| || | logical or; test at least one condition |
| ! | Logical not; takes single boolean value and inverts it |
n order for JavaScript to compare two different data types (for example, numbers and strings), it must convert one type to another. This is known as “Type Coercion”
Chapter 4: “Decisions and Loops” only up to the section on switch statements (pp.145-162)
Operators
| keyword | Description |
|---|---|
| == | is equal to |
| != | is not equal to |
| === | strict equal to |
| !== | strict not equal to |
| > | greater than |
| < | less than |
| >= | greater than or equal to |
| <= | less than or equal to |
| && | logical and; test more than one condition |
| || | logical or; test at least one condition |
| ! | Logical not; takes single boolean value and inverts it |
logical evaluation are done from left to right
If Statements
if statements - tells JavaScript to execute the code in the curly braces under certain conditions, defined in the parentheses.
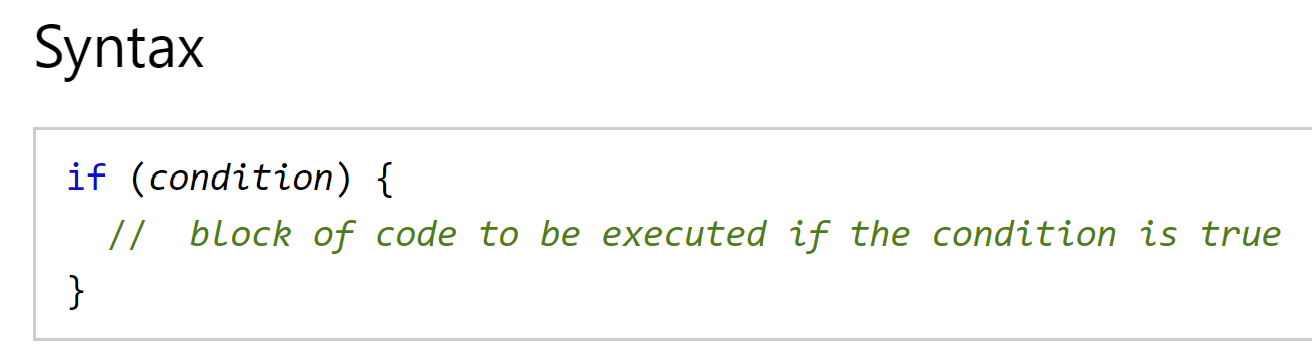 Courtesy of W3 schools
Courtesy of W3 schools